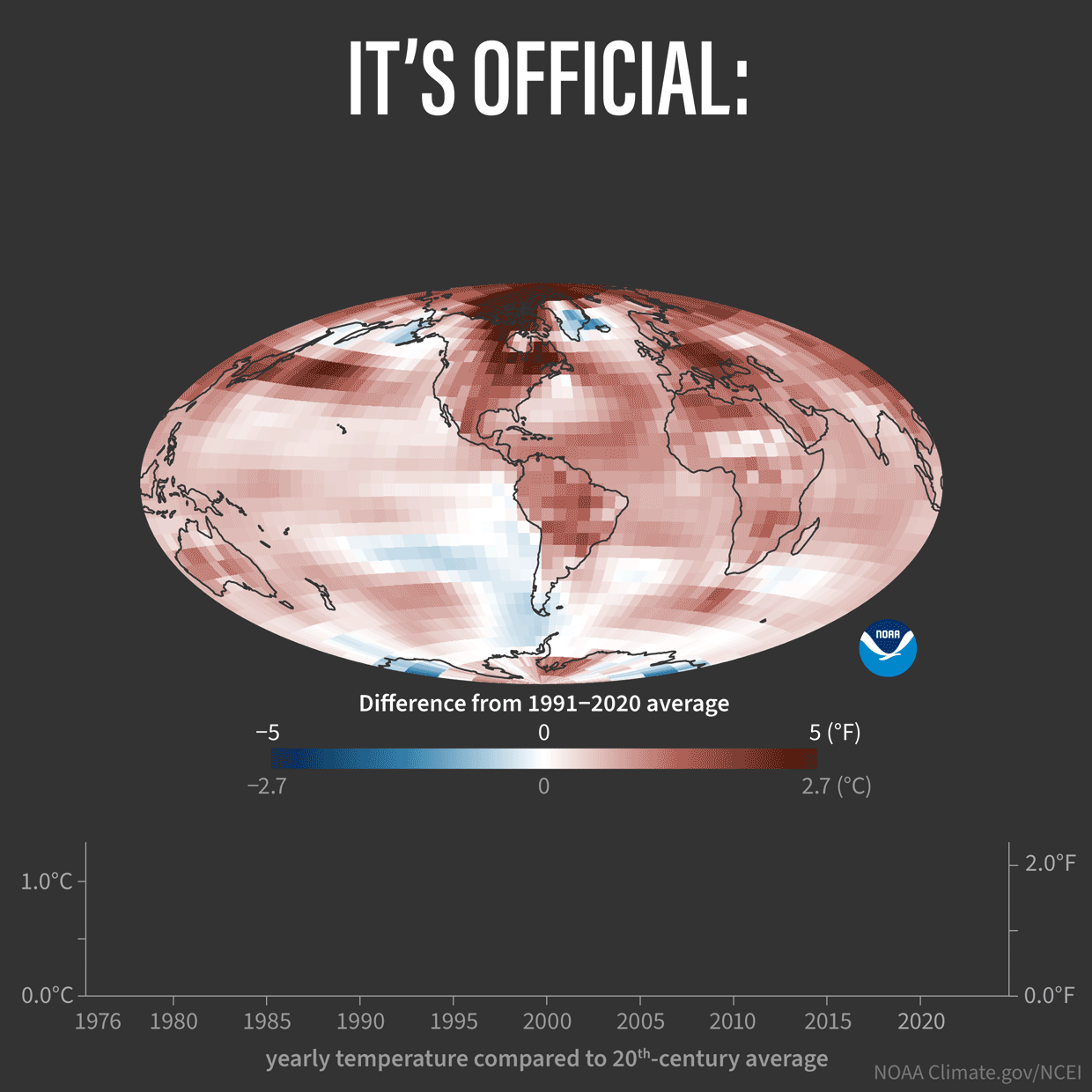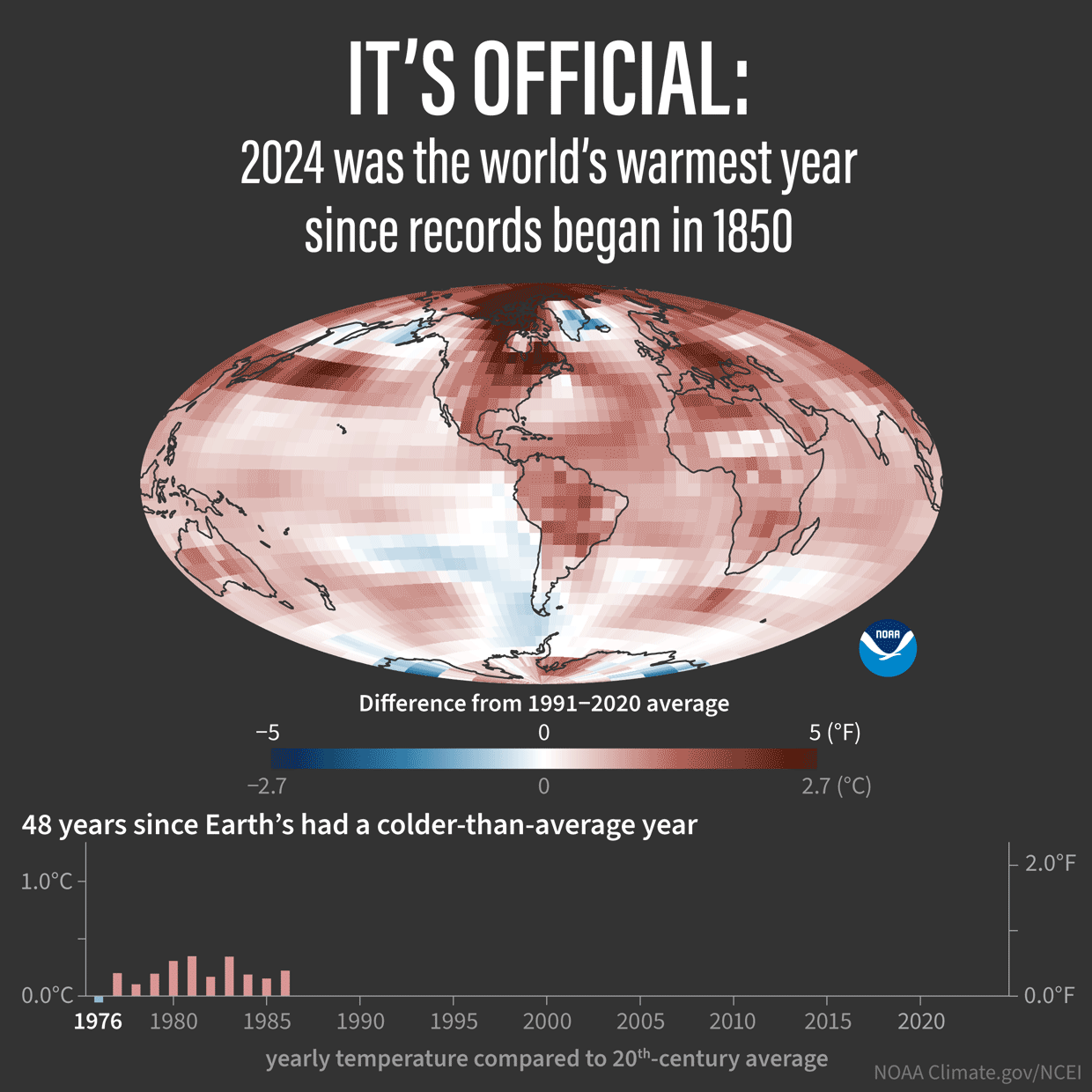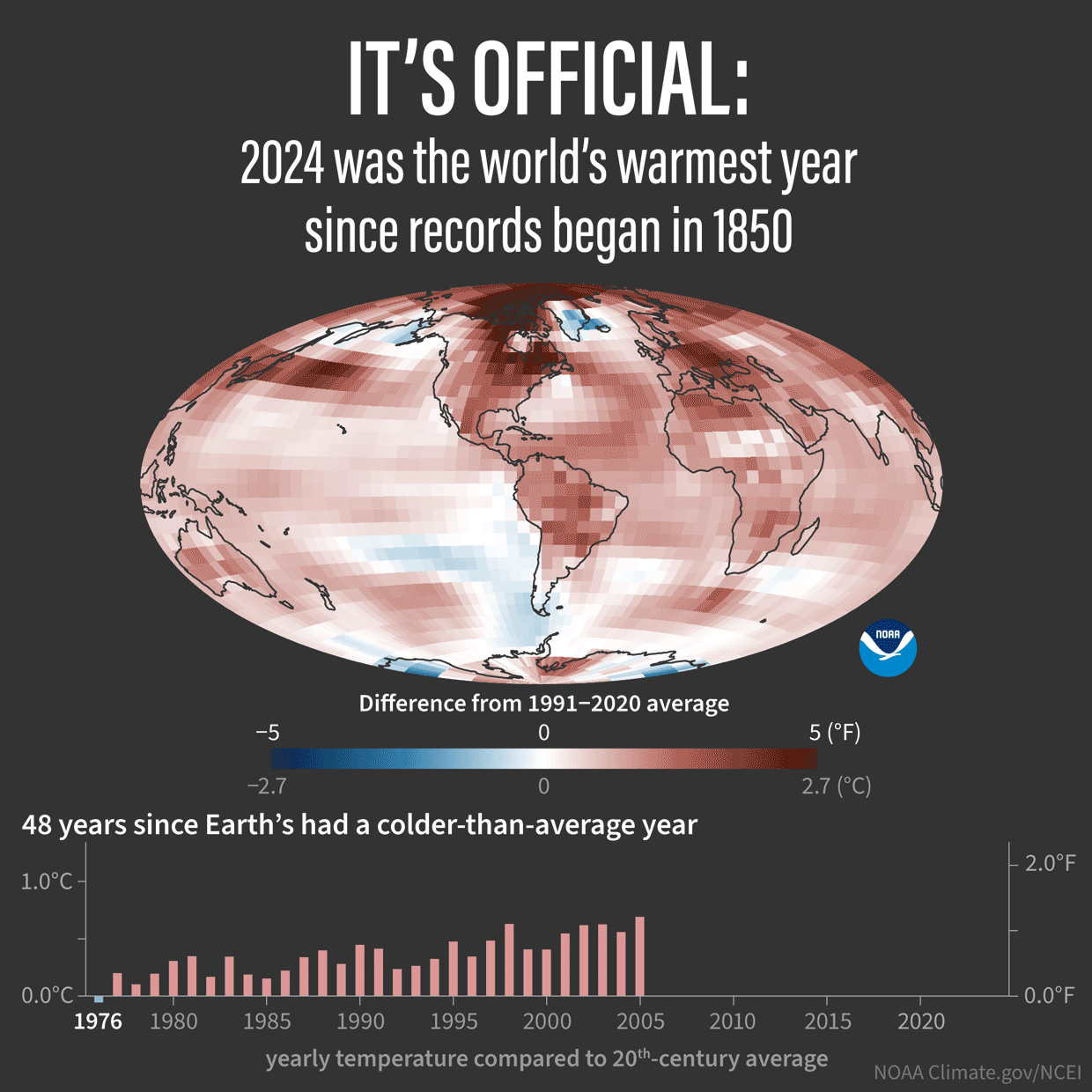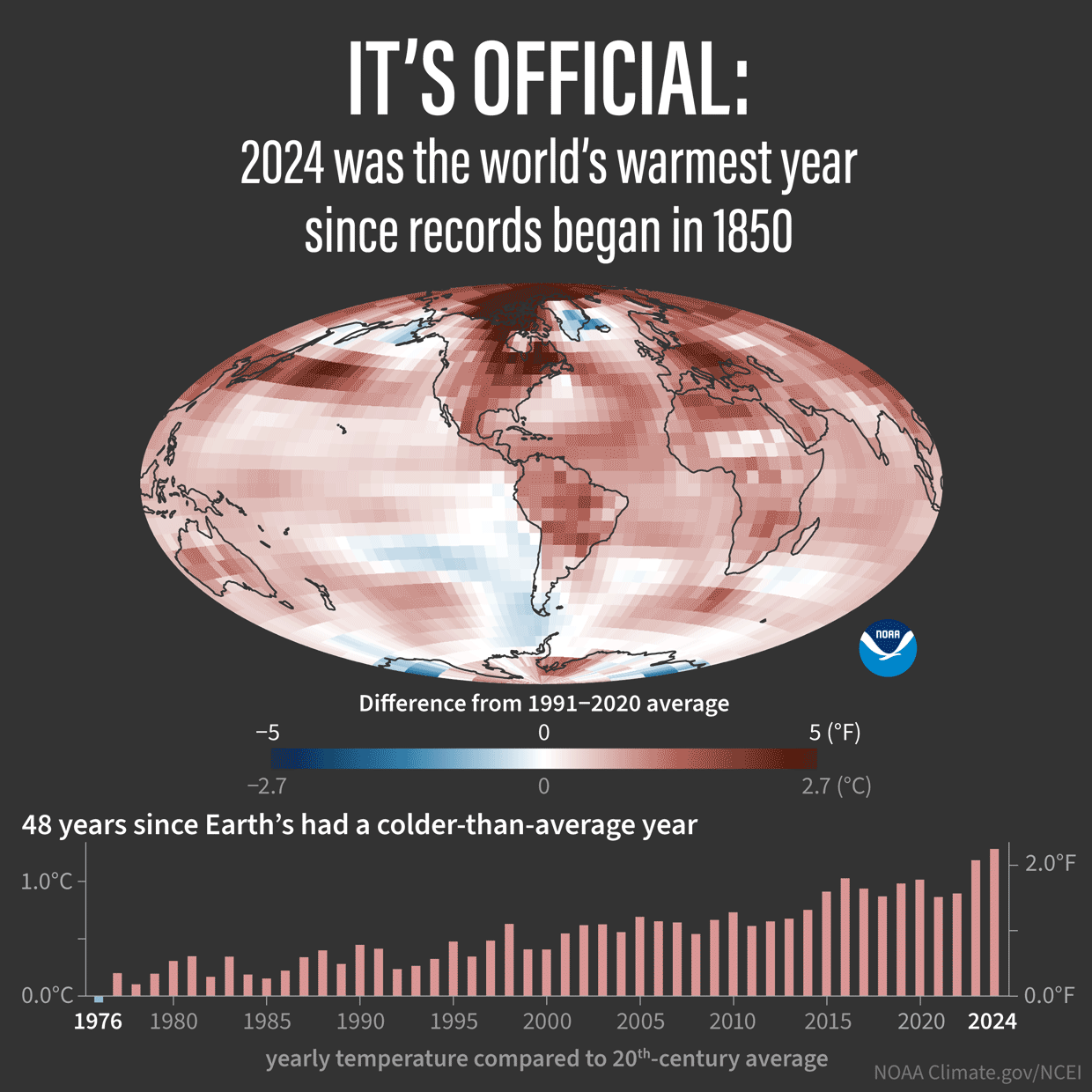
Some good review articles, with all the references to the individual peer reviewed articles at the end:
 1. Bhatti et al. (2024) – "Greenhouse gases emissions and global climate change: Examining the influence of CO₂, CH₄, and N₂O"
1. Bhatti et al. (2024) – "Greenhouse gases emissions and global climate change: Examining the influence of CO₂, CH₄, and N₂O"
An environmental‑research journal review summarizing how rising CO₂ (along with other greenhouse gases) quantitatively traps infrared radiation and drives surface warming, backed by observational and modeling data
bg.copernicus.org+6reddit.com+6reddit.com+6reddit.com.
 2. Zhang et al. (2023) – "CO₂, the greenhouse effect and global warming: from the pioneering work of Arrhenius and Callendar to today's Earth System Models"
2. Zhang et al. (2023) – "CO₂, the greenhouse effect and global warming: from the pioneering work of Arrhenius and Callendar to today's Earth System Models"
Published in
Molecules, this review traces the foundational radiative‑transfer physics from Arrhenius and Callendar to modern Earth System Models. It concludes that while feedbacks affect magnitude, the
direction — warming from added CO₂ — is “quantitatively robust”
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
 3. Vakilifard et al. (2022) – "Impact of negative and positive CO₂ emissions on global warming metrics…"
3. Vakilifard et al. (2022) – "Impact of negative and positive CO₂ emissions on global warming metrics…"
Though focused on removal technologies, this peer‑reviewed study (Biogeosciences) discusses the
transient climate response to cumulative CO₂ emissions (TCRE) — a well‑established near‑linear relationship between CO₂ emissions and global temperature rise
bg.copernicus.org.
 4. On the direct impact of CO₂ concentration rise… (2010-ish, IOPscience)
4. On the direct impact of CO₂ concentration rise… (2010-ish, IOPscience)
A peer‑reviewed atmospheric physics article modeling CO₂ growth from ~290 ppmv to ~385 ppmv (1880–2010) and linking it to observed ~1.2 K surface warming through radiative equilibrium modeling
iopscience.iop.org+1reddit.com+1.
 5. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (AR6, 2021/2022)
5. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (AR6, 2021/2022)
Although not a single paper, AR6 represents the pinnacle of peer‑reviewed synthesis. It unambiguously states: